What is titanium dioxide?
The main component of titanium dioxide is TIO2, which is an important inorganic chemical pigment in the form of a white solid or powder. It is non-toxic, has high whiteness and brightness, and is considered the best white pigment for improving material whiteness. It is widely used in industries such as coatings, plastics, rubber, paper, ink, ceramics, glass, etc.

Ⅰ.Titanium dioxide industry chain diagram:
(1)The upstream of the titanium dioxide industry chain consists of raw materials, including ilmenite, titanium concentrate, rutile, etc;
(2)The midstream refers to titanium dioxide products.
(3)The downstream is the application field of titanium dioxide.Titanium dioxide is widely used in various fields such as coatings, plastics, papermaking, ink, rubber, etc.

Ⅱ.The crystal structure of titanium dioxide:
Titanium dioxide is a kind of polymorphous compound, which has three common crystal forms in nature, namely anatase, rutile and brookite.
Both rutile and anatase belong to tetragonal crystal system, which are stable under normal temperature; brookite belongs to orthorhombic crystal system, with unstable crystal structure, so it has little practical value in industry at present.

Among the three structures, rutile phase is the most stable one. Anatase phase will irreversibly transform into rutile phase above 900°C, while brookite phase will irreversibly transform into rutile phase above 650°C.
(1)Rutile phase titanium dioxide
In rutile phase titanium dioxide, Ti atoms are located at the center of the crystal lattice, and six oxygen atoms are located at the corners of the titanium-oxygen octahedron. Each octahedron is connected to 10 surrounding octahedrons (including eight sharing vertices and two sharing edges), and two TiO2 molecules form a unit cell.
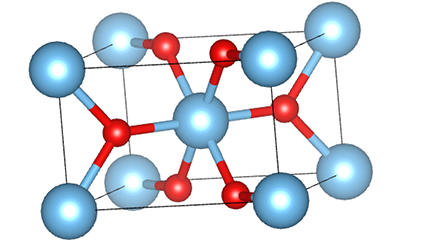
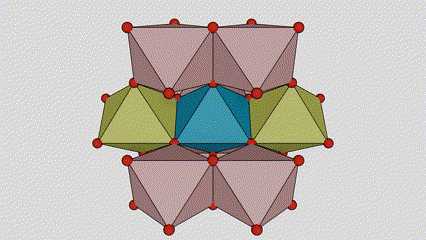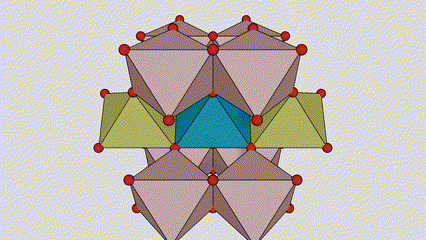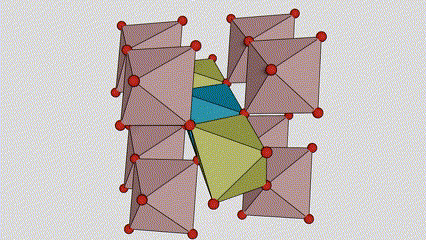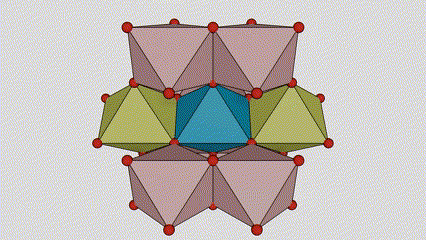
Schematic diagram of crystal cell of rutile phase titanium dioxide (left)
The connection method of titanium oxide octahedron (right)
(2)Anatase phase titanium dioxide
In anatase phase titanium dioxide, each titanium-oxygen octahedron is connected to 8 surrounding octahedrons (4 sharing edges and 4 sharing vertices), and 4 TiO2 molecules form a unit cell.
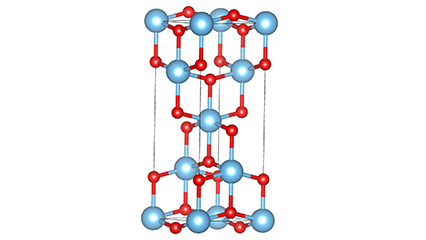
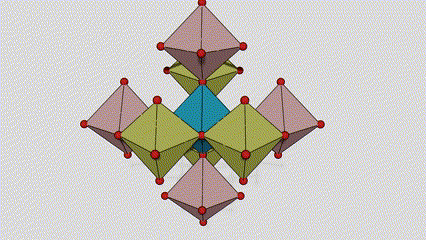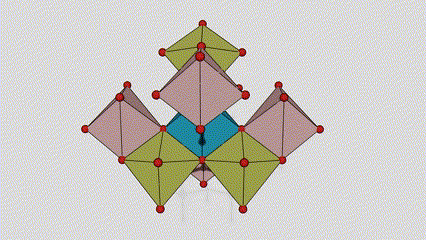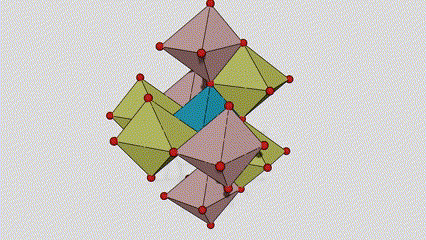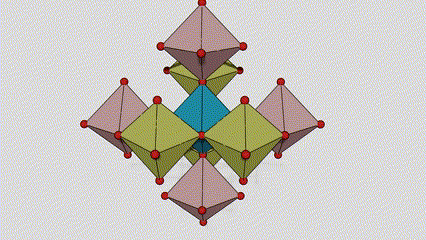
Schematic diagram of crystal cell of rutile phase titanium dioxide (left)
The connection method of titanium oxide octahedron (right)
Ⅲ.Preparation Methods of Titanium Dioxide:
The production process of titanium dioxide mainly includes sulfuric acid process and chlorination process.

(1)Sulfuric acid process
The sulfuric acid process of titanium dioxide production involves the acidolysis reaction of titanium iron powder with concentrated sulfuric acid to produce titanium sulfate, which is then hydrolyzed to produce metatitanic acid. After calcination and crushing, titanium dioxide products are obtained. This method can produce anatase and rutile titanium dioxide.
(2)Chlorination process
The chlorination process of titanium dioxide production involves mixing rutile or high-titanium slag powder with coke and then carrying out high-temperature chlorination to produce titanium tetrachloride. After high-temperature oxidation, the titanium dioxide product is obtained through filtration, water washing, drying, and crushing. The chlorination process of titanium dioxide production can only produce rutile products.
How to distinguish the authenticity of titanium dioxide?
I. Physical Methods:
(1) The simplest method is to compare the texture by touch. Fake titanium dioxide feels smoother, while genuine titanium dioxide feels rougher.

(2)By rinsing with water, if you put some titanium dioxide on your hand, the fake one is easy to wash off, while the genuine one is not easy to wash off.

(3) Take a cup of clean water and drop titanium dioxide into it. The one that floats to the surface is genuine, while the one that settles to the bottom is fake (this method may not work for activated or modified products).
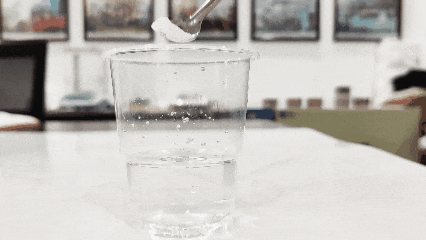

(4)Check its solubility in water. Generally, titanium dioxide is soluble in water (except for titanium dioxide specifically designed for plastics, inks, and some synthetic titanium dioxide, which are insoluble in water).
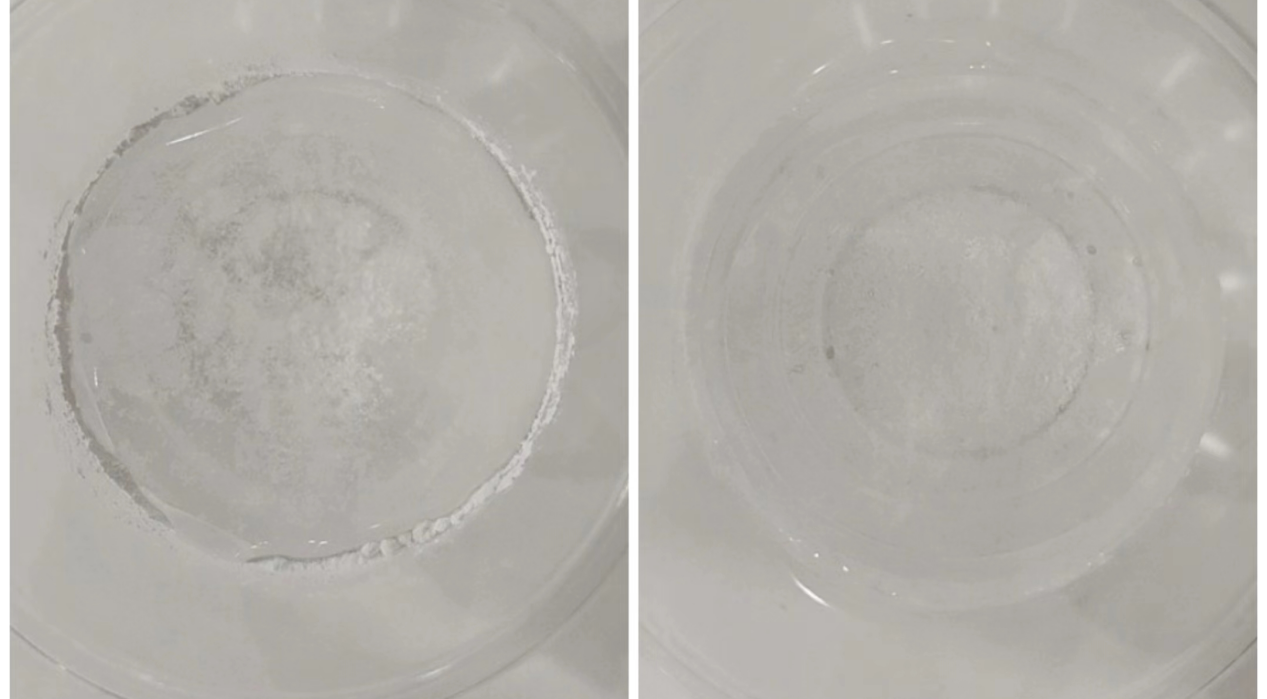

II. Chemical methods:
(1) If calcium powder is added: Adding hydrochloric acid will cause a vigorous reaction with a squeaking sound, accompanied by the production of a large number of bubbles (because calcium carbonate reacts with acid to produce carbon dioxide).

(2) If lithopone is added: Adding dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid will produce a rotten egg smell.

(3) If the sample is hydrophobic, adding hydrochloric acid will not cause a reaction. However, after wetting it with ethanol and then adding hydrochloric acid, if bubbles are produced, it proves that the sample contains coated calcium carbonate powder.

III. There are also two other good methods:
(1) By using the same formula of PP + 30% GF + 5% PP-G-MAH + 0.5% titanium dioxide powder, the lower the strength of the resulting material is, the more authentic the titanium dioxide (rutile) is.
(2) Select a transparent resin, such as transparent ABS with 0.5% titanium dioxide powder added. Measure its light transmittance. The lower the light transmittance is, the more authentic the titanium dioxide powder is.
Post time: May-31-2024





